Running Trinity on DappNode¶
Trinity can be installed as a DappNode package which is a very convenient way to permanently keep a node running at home. It’s also a nice option for developers to test new code in an environment that is meant for running these nodes in production.
Installation¶
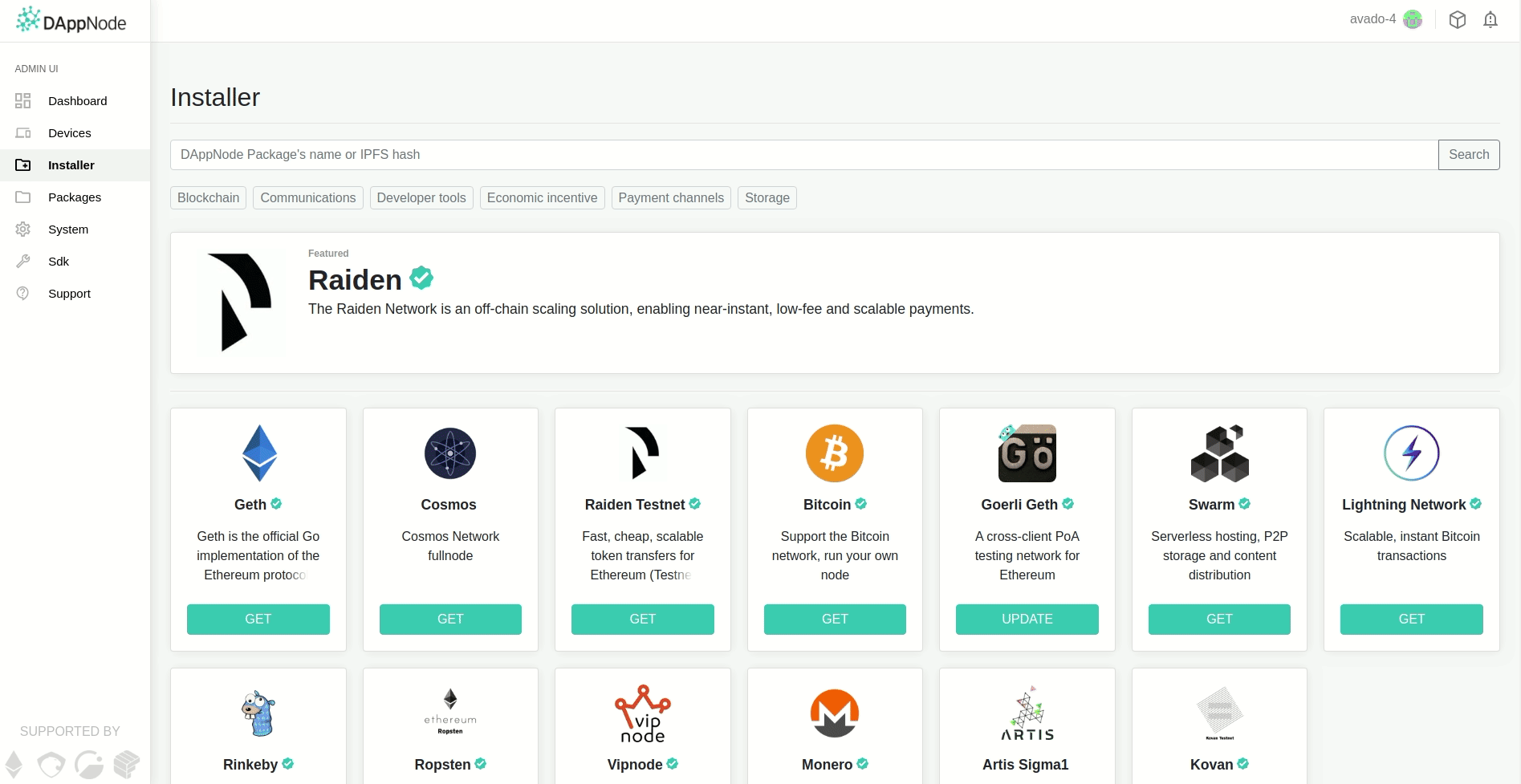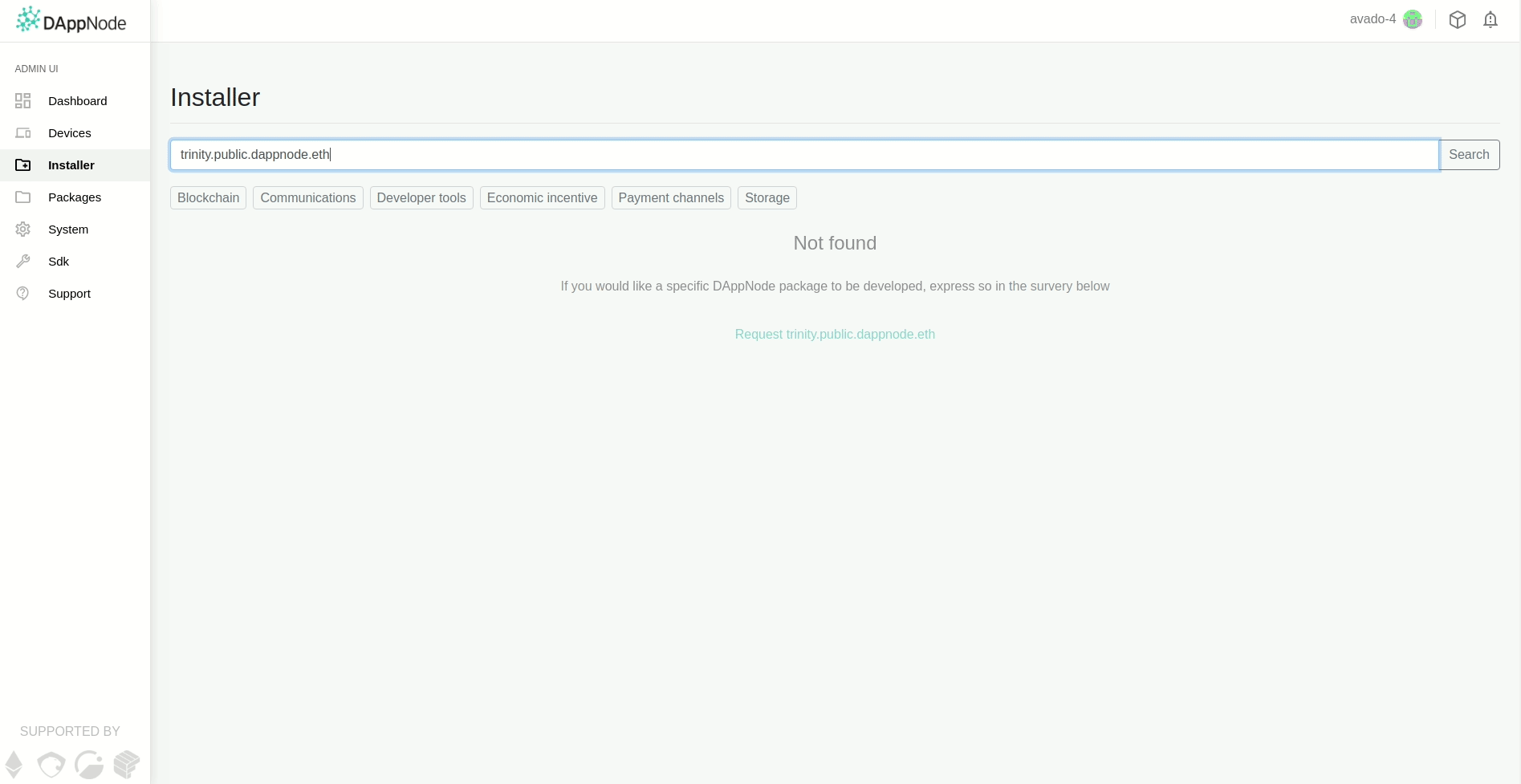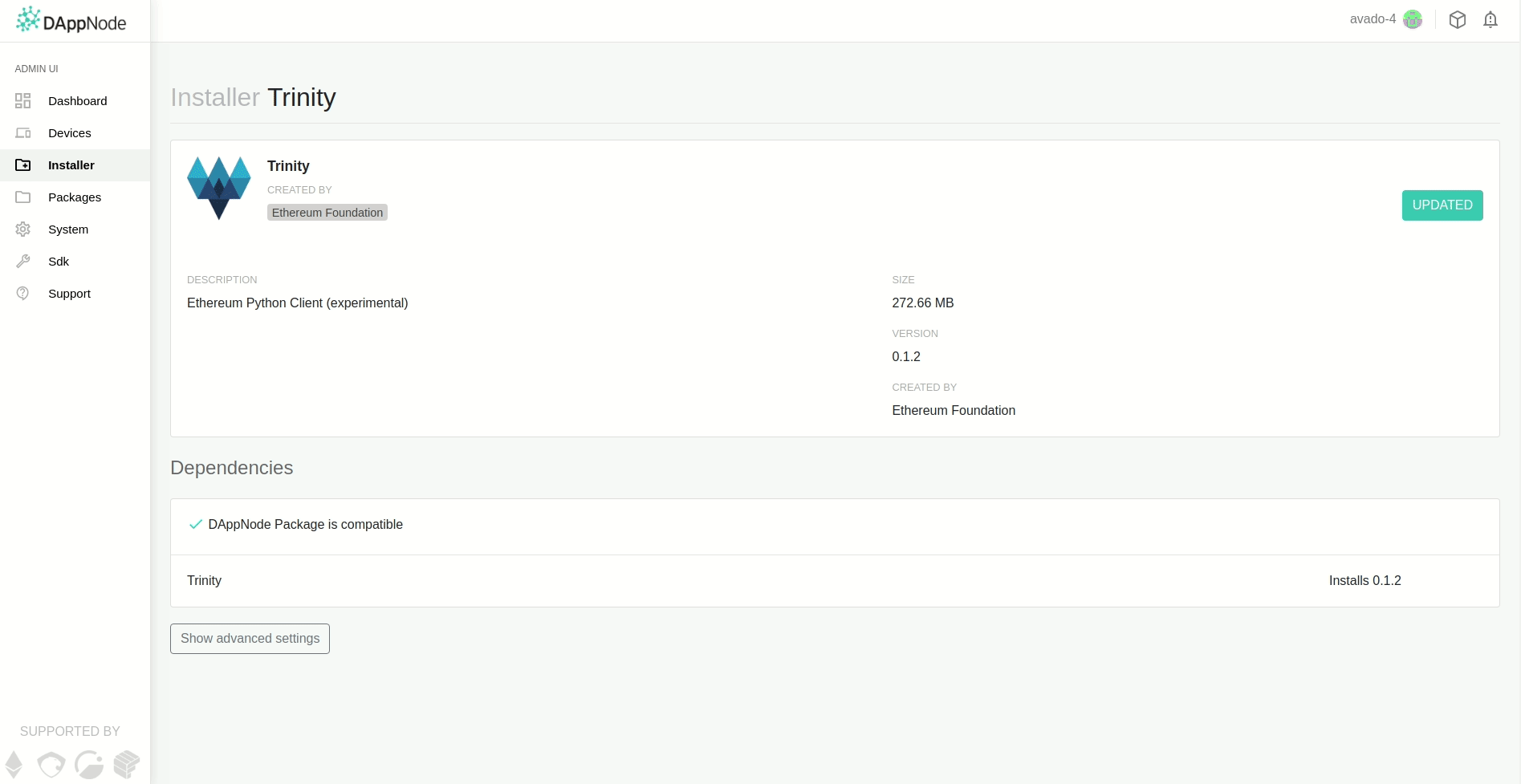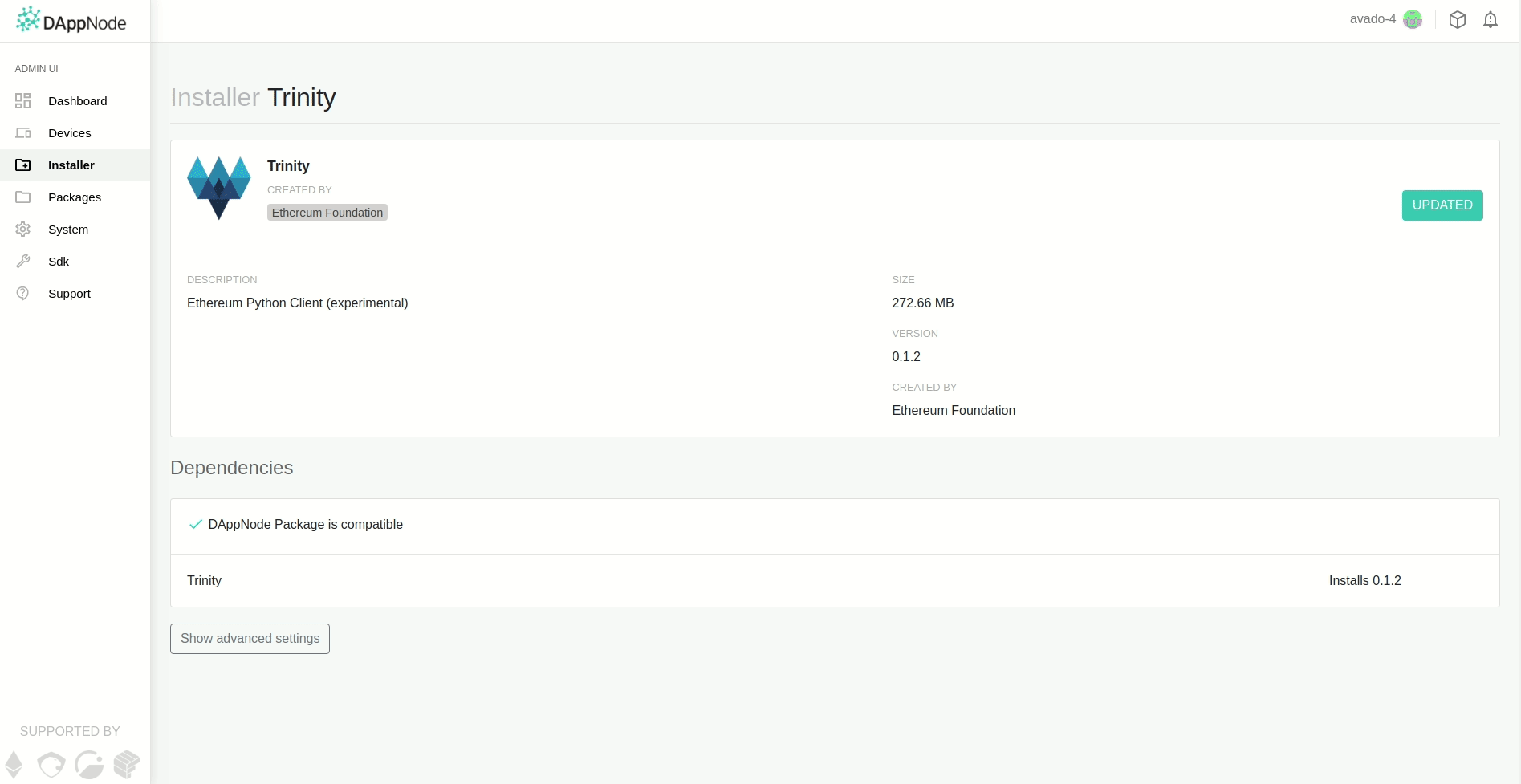
We install Trinity like any other DappNode package by looking up its package name on the
Installer page. It is found by the name trinity.public.dappnode.eth as shown in the
animation below.
Note
Upgrading from a previous version may not work as expected. If the version that Trinity reports on startup doesn’t match our expectations, uninstall any currently installed version and reinstall the new version rather than upgrading from an existing version.
After Trinity is installed, it will immediately try to find peers and start syncing.
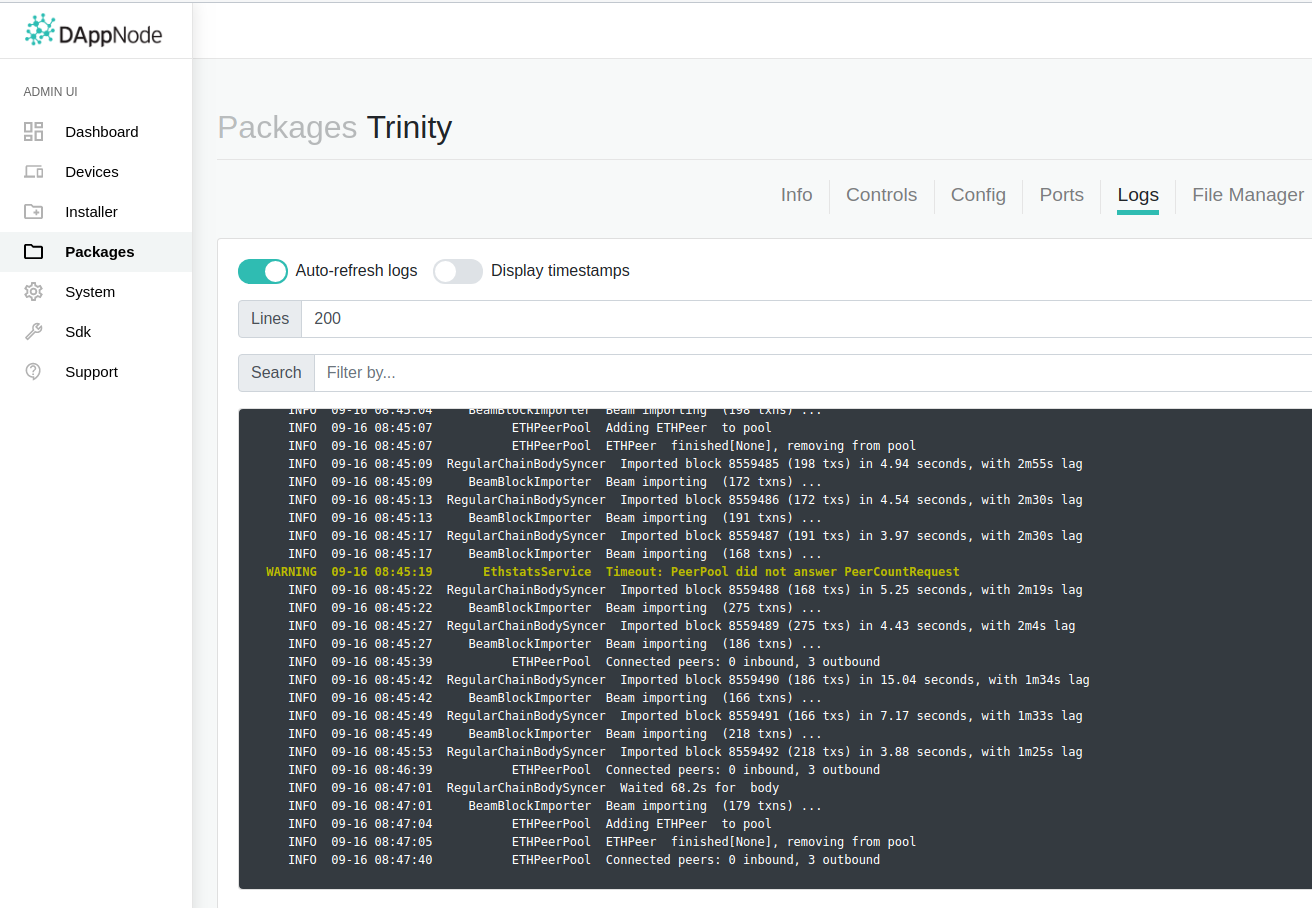
Configuration¶
Configuring Trinity on DappNode is very easy. We can set all CLI flags through the Config page of the package as shown below.
Trinity will automatically reboot using the new parameters whenever we save any changes on the Config page.
Note
Changing or removing the --trinity-root-dir configuration from its default value
trinity will cause us to lose the ability to easily inspect all Trinity related
files from the host machine.
Connecting to the local Geth node¶
By design, DappNode runs a local Ethereum node to provide various core services. Unless changed manually, that node will be running the popular Geth client.
To ensure we get the best performance out of our Trinity node, we should find out the
enode of our Geth node and set it as --preferred-node <local-geth-enode> in Trinity’s
startup parameters.
Finding Geth’s enode¶
There are two ways how we can find out the enode of our local Geth node. One would be to
restart the Geth package and watch for the enode getting printed to the logs view during
boot.
Instead we can also make a request against the admin_nodeInfo API of the JSON-RPC interface.
Note, that we need to enable the admin module in the Config page of the Geth node for
that request to work.
Run:
curl http://geth.dappnode:8545 -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{ "method": "admin_nodeInfo", "params": [], "id": 1, "jsonrpc": "2.0" }'
The output will look roughly like this:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"id": "a80a1d052260071fbc1ea084aa8f48ff4ff4c60060d7962f4652027cd21f2bd8",
"name": "Geth/v1.9.18-stable-f5382591/linux-amd64/go1.14.6",
"enode": "enode://ef33809deedbeefbb60a5724f51640ade542145228abfd59bf21268c6195ca3d38832f9c831e64ea22bb1e9b0b5ded26df2b0a001c9ffb13d9041ae45032c9d3@73.137.153.35:30303",
"enr": "enr:-Je9QBlOpjIXHW0npnk1k-fPPg5mUzDF-9X-iCl8AFATTf8zBTUuGrJhtN0PlWwfACmCNa4FABS8Rc26lU6klq5ws04Zg2V0aMfGhOAp6ZGAgmlkgnY0gmlwhF3vlyWJc2VjcDI1NmsxoQPUBi34u2Clck-Kv9pNOINe8zgJFkCt5UIUUiL5yFm_IYN0Y3CCdl-DdWRwgnZf",
"ip": "93.239.151.37",
"ports": {
"discovery": 30303,
"listener": 30303
},
"listenAddr": "[::]:30303",
...
}
}
We can take the enode from the result but notice that it shows our external IP address. If we do have a
static IP address then there’s nothing to worry about. If however, our external IP address changes (like with
most home routers), we should replace the IP address in that enode with the local IP address of
the Geth node (every node runs in a separate docker container behind it’s own local IP address).
To find the local IP address of our Geth node we can run something like:
curl http://geth.dappnode:8545 -v
The output hints us the IP address behind our Geth node.
* Trying 172.33.0.4:8545...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to geth.dappnode (172.33.0.4) port 8545 (#0)
To continue with Geth’s local IP address we change the enode to
enode://ef33809deedbeefbb60a5724f51640ade542145228abfd59bf21268c6195ca3d38832f9c831e64ea22bb1e9b0b5ded26df2b0a001c9ffb13d9041ae45032c9d3@172.33.0.4:30303
Obviously, this ☝️ is an example enode and IP address and everyone’s will look different.
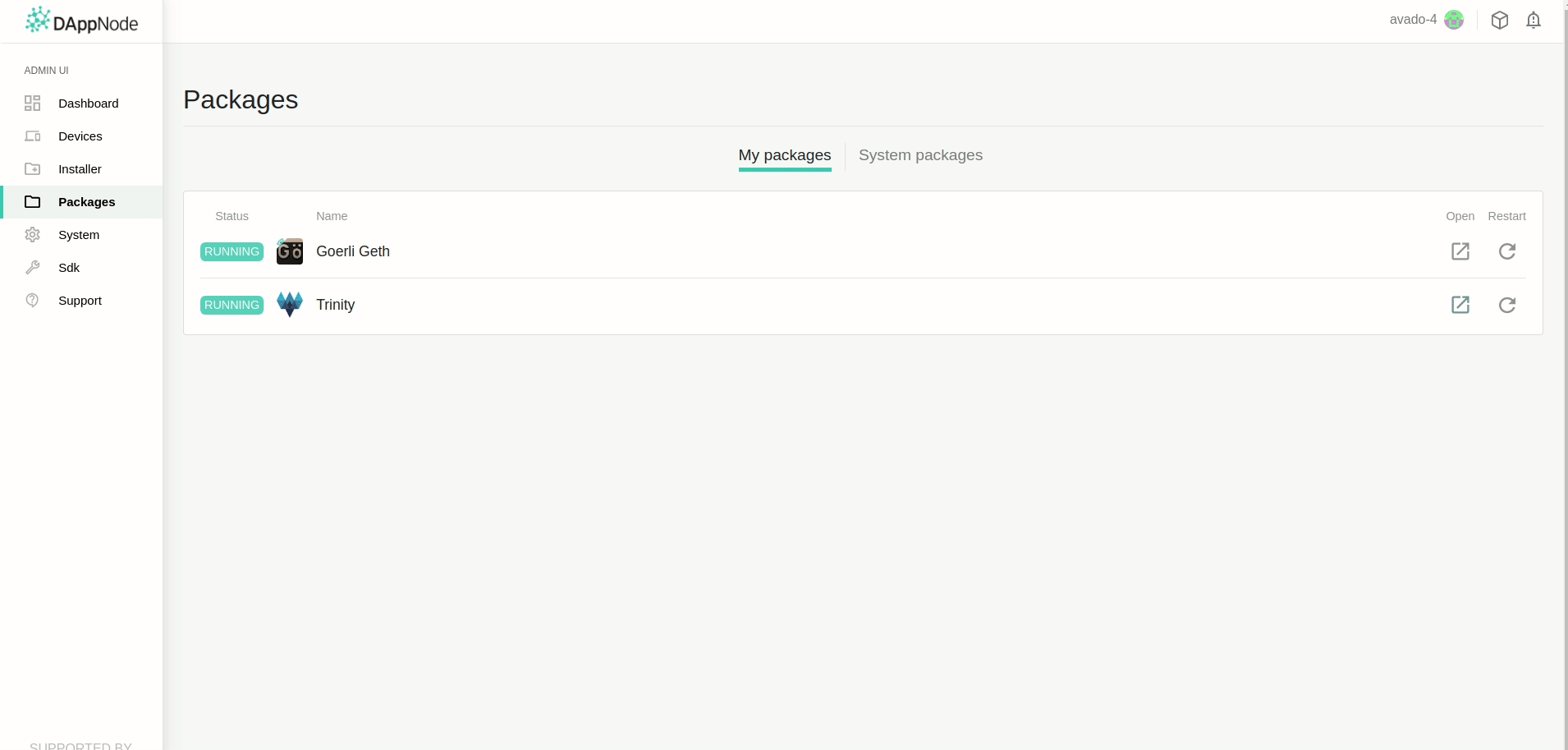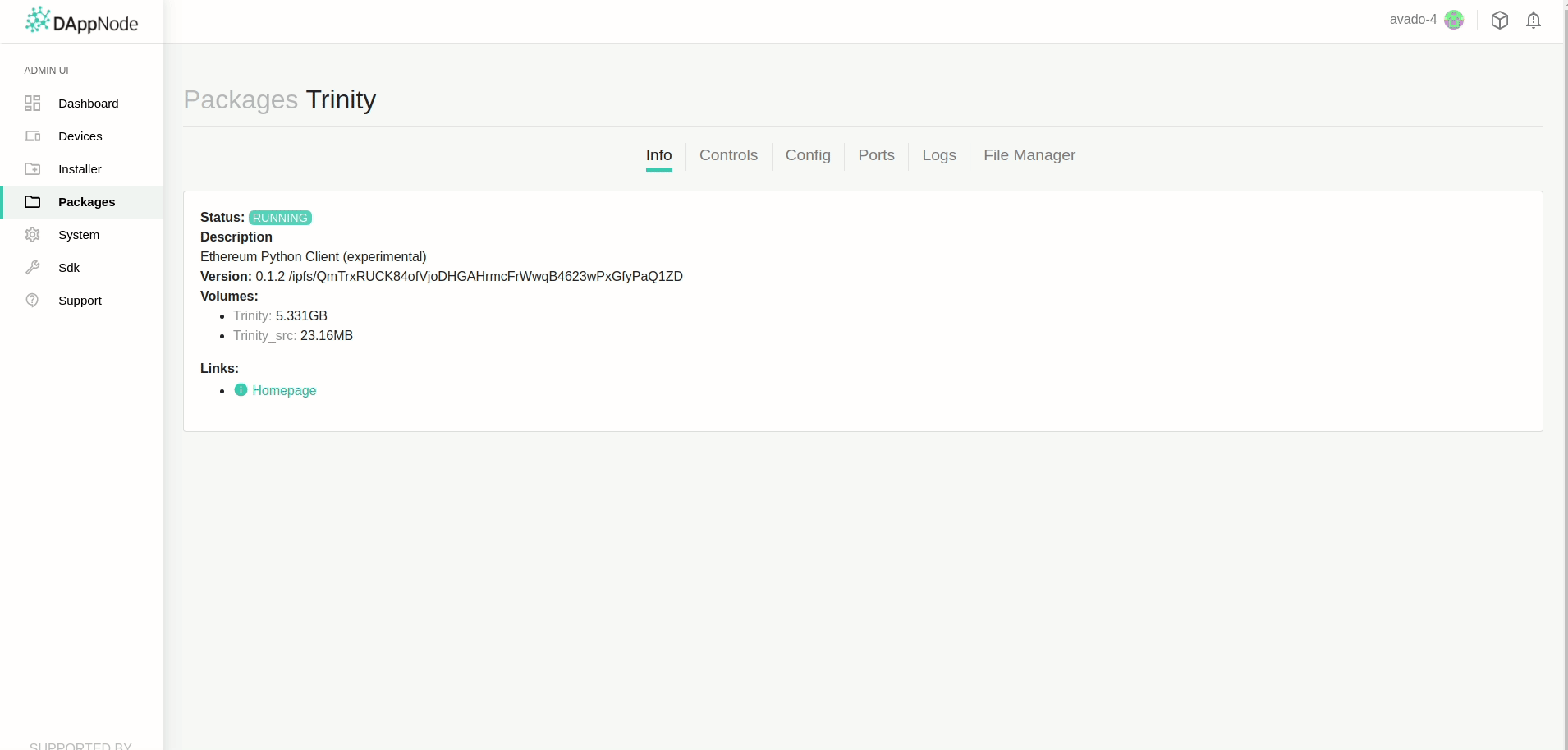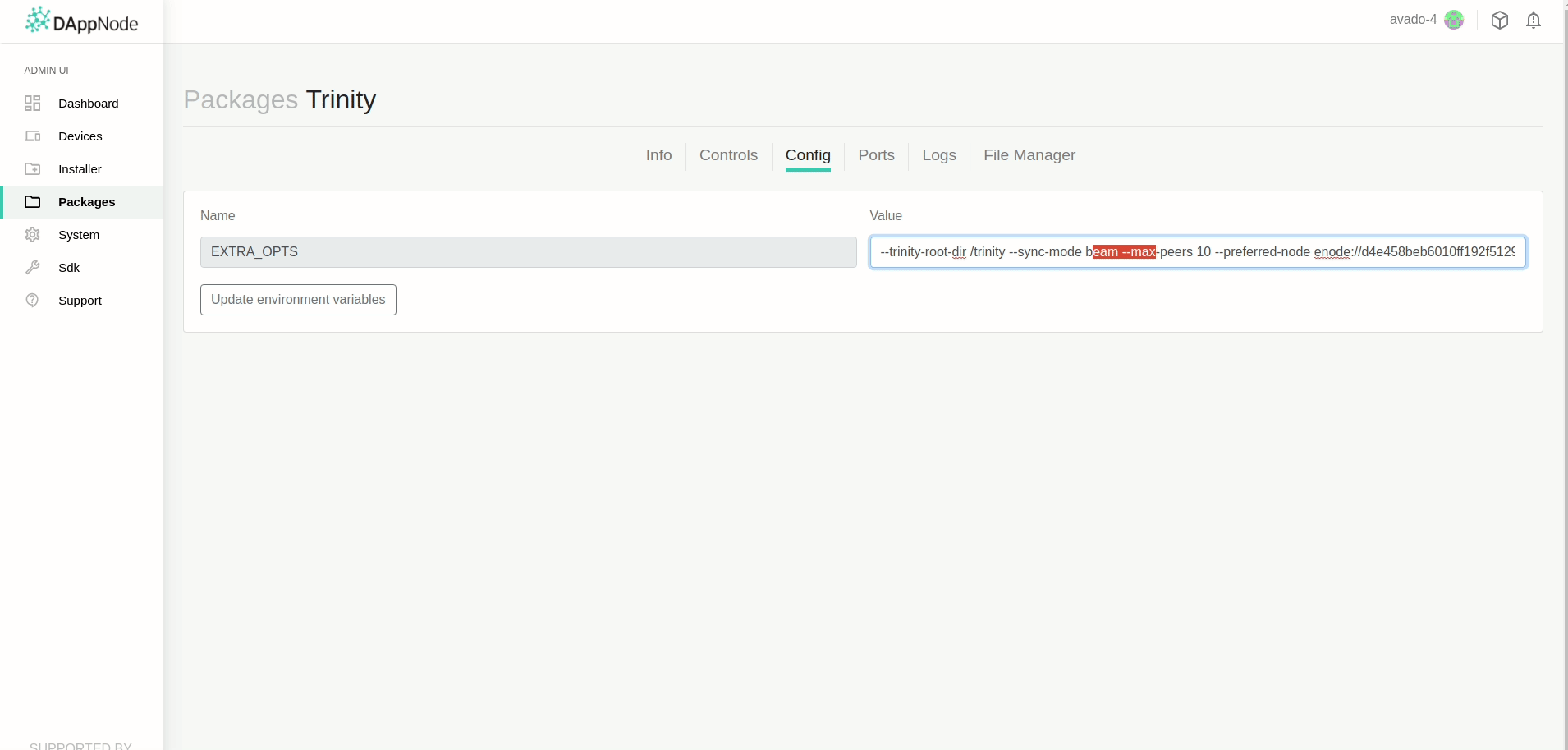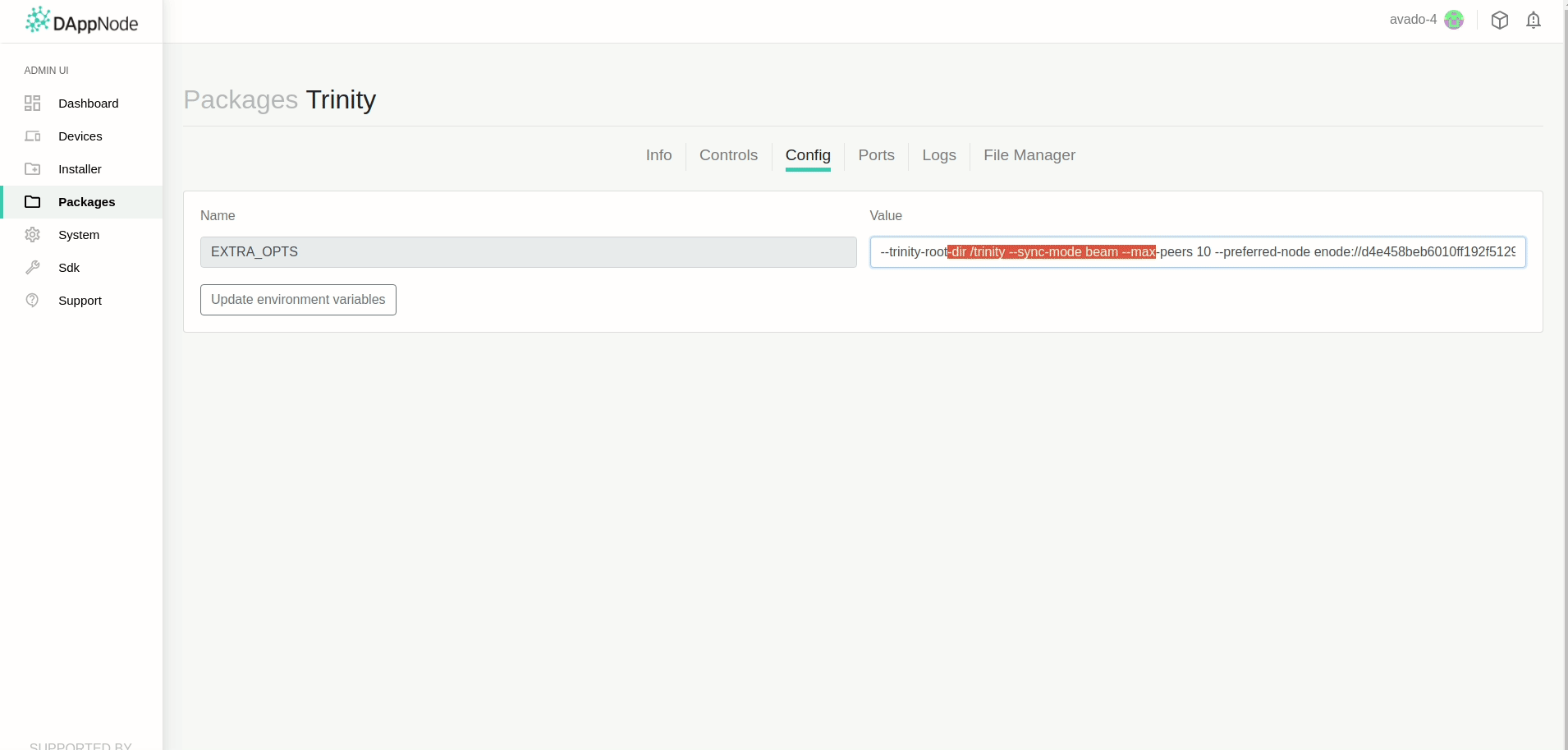
Setting the preferred node¶
Now that we have obtained the enode (either with local or external IP address) we need to go
to the Config tab of the Trinity package and append it to the existing value of the
EXTRA_OPTS configuration key.
For example, if the current value is:
--trinity-root-dir /trinity --enable-http-apis=net,eth --http-listen-address 0.0.0.0
Change it to
--trinity-root-dir /trinity --enable-http-apis=net,eth --http-listen-address 0.0.0.0 --preferred-node enode://ef33809deedbeefbb60a5724f51640ade542145228abfd59bf21268c6195ca3d38832f9c831e64ea22bb1e9b0b5ded26df2b0a001c9ffb13d9041ae45032c9d3@172.33.0.4:30303
Then click Update and Trinity will reboot and try to connect to our local Geth node.
Ensuring Geth treats us well¶
Depending on the current circumstances within the DappNode’s Geth node there’s a chance it would not accept our Trinity node as a new peer (e.g. because it has reached its maximum peer capacity).
We can make sure to always get a free pass no matter what. To do that we have to declare our Trinity node as a trusted peer at the Geth node.
To do that, we first have to find Trinity’s enode. Just like we did with the Geth node, we can either read
Trinitys enode from the log view while it is booting or use the admin_nodeInfo API to find it.
Also, just as we did with Geth, we can figure out Trinity’s local IP address by running.
curl http://trinity.public.dappnode:8545 -v
Notice that Trinity’s port is not the default one. Since DappNode runs multiple Ethereum nodes on the same
device only the system Ethereum node gets the default port whereas Trinity is reachable on port 57313.
Now that we have Trinity’s enode we can call Geth’s admin_addTrustedPeer API.
curl http://geth.dappnode:8545 -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{ "method": "admin_addTrustedPeer", "params": ["enode://ef33...5032@172.33.0.2:57313"], "id": 1, "jsonrpc": "2.0" }'
That’s it. Trinity now has a special green card to always connect to DappNode’s system node.
Accessing data¶
The data that Trinity creates when it runs is stored in a directory outside the core application files. It is mapped as a volume to be preserved across package updates to not lose previously synced blockchain data, knowledge about peers, written logs etc.
The volume can be found under /var/lib/docker/volumes/trinitypublicdappnodeeth_trinity.
Downloading logs from the DappNode¶
We may also fetch any files including logs from our Dappnode with the command shown below.
scp root@<ip-of-dappnode>:/var/lib/docker/volumes/trinitypublicdappnodeeth_trinity/_data/mainnet/logs-eth1/trinity.log /tmp/trinity_dappnode.log